Liberalising China - GDP



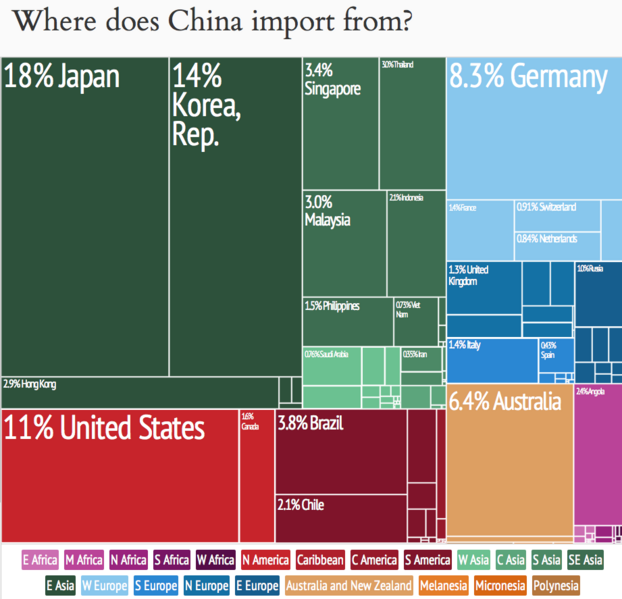
This shows that China exports substantially to the United States (their largest exporter) as well as a substantial amount to Hong Kong, Japan, Germany and Korea.
Joint Venture
Interest Rate
 The benchmark interest rate in China was last reported at 6.31 %,
The benchmark interest rate in China was last reported at 6.31 %,
Exchange Rate

Exchange rates play such an important role in a country's competiveness level, currency exchange rates are among the most analysed and forecasted indicators in the world. The exchange rate is determined by the level of supply and demand on the international markets. However, changes in foreign exchange market rates are often difficult to understand and to predict because the market is very large and volatile.
This grap shows that the USD-CNY spot exchange rate appreciated 0.0030 or 0.05 percent during the last few months. Historically, from 1981 until 2012, the USD-CNY averaged 7.0100 reaching an all time high of 8.7300 in January of 1994 and a record low of 1.5300 in January of 1981.
• China's economy has been
flourishing and expanding rapidly over the past few years compared to many
other economies around the globe. In 2010, China's GDP growth was 10.456%
and is expected to increase to 11.79% in 2011; from US $5,745.13 billion to US
$6,422.28 billion. Forecasting a growth of 10-12% each year between 2010 and
2015.
• China; the second biggest economy
in the world after the Unites States has witnessed miraculous growth over the
last 30 years. Averaging 8% growth in GDP per annum, the fastest growing
economy in the world; analysts have predicted that it will become the largest
economy in the world this century.
| GDP | $12.46 trillion (PPP: 2nd; 2012)[2] |
|---|---|
| GDP growth | 9.5% (major economies: 2nd; 2011)[3] |
| GDP per capita | $8,394 (PPP: 90th; 2011)[2] |
| GDP by sector | Industry (46.8%), services (43.6%), agriculture (9.6%) (2010 est. |
Population
• Being the most populous country,
China has a population of 1.3 billion (as of 2011), representing 20% of the
world's population. The population of China grew dramatically from the
early 1980's; having a mere population of only 563 million in the 1950's.
• It is predicted that by 2030,
China's population is expected to start dropping slowly; while India (the
second most populous country) is expected to surpass China in population.
• The one child policy was
initiated in 1978 to help keep China's population under control; although it is
only 35.9% of China's population that are subjected to the one child
population, the policy has prevented over 400 million births from 1979 to 2011.
• The one child policy has reduced
the demand of natural resources, maintaining a steady labour rate leading to reduction in unemployment.


Imports and Exports
Importing refers to bringing in an outside source, in particular bringing in goods or materials from a foreign country for trade or sale. Whereas Exporting refers to send or transport also in particular goods and commodities for trade or sale.
• China exported US$287.8 billion
worth of merchandise to the United States in 2006, up 18.2% from 2005 and up an
impressive 130% in just 4 years. America is the number one trading partner for
China's exports.
• Zinc, nickel, lumber, mining
& oil equipment lead China's fastest-growing exports to U.S. while tobacco,
corn & precious metals are popular American imports in China.
• In terms of the merchandise flow between the two
countries, America’s trade deficit with China was $232.5 billion in 2006, up
125% from 2002. The U.S. trade deficit with China increased 15.4% in 2006 –
significantly down from the 24.5% deficit increase in 2005 from the year
earlier.
China has varied products to export - you name it - toys, electronic gadgets, home appliances, shoes, clothes, food products, seafood, body jewelry, kitchenware, bags and much more. China is the world's leading producer of items made from plastic, and Western countries such as the US are a ready market. China also sells armaments to many countries around the world.
Because of its huge manpower resource China is able to manufacture products at a competitive advantage. Other developing countries have a similar labor cost advantage. But the communist government also controls employment, prices, and wages, and can actively subsidize any commercial activity that benefits their economy.
Because of its huge manpower resource China is able to manufacture products at a competitive advantage. Other developing countries have a similar labor cost advantage. But the communist government also controls employment, prices, and wages, and can actively subsidize any commercial activity that benefits their economy.
Seven countries are among both China's top
exporters and top importers. Of those, China exports more than it imports from
three countries and is therefore in a surplus position.


12 Facts about their Economy
1. At this moment, China’s
economy is the third largest in the world, just behind the United
States and Japan.
2. With a GDP of $4.91 trillion,
it is fast becoming the biggest economy on the planet and it has the second
highest net-worth behind the United States with $8.77 trillion.
3. China has the fastest growing
major economy on the planet, with a 10 percent growth rate over the past
30 years on average per year.
4. China may be a huge economy,
but its per capita income is only $3,677, which puts it 97th in the world.
5. That will change as time goes
on though because China is the second-largest trading nation in the world, and
the largest exporter, while also being the second largest importer
6. The growth of China’s economy
has also helped its citizens come out of poverty. The level of
poverty in China fell from 53 percent in 1981, to 2.5 percent in 2005.
7. The infant mortality rate has
also fallen as China has grown in economic power, falling roughly 39 percent
between 1990 and 2005.
8. China has a lot of trade
going through its borders, and its currency is highly traded on the world's
markets.
9. Currently, the foreign
exchange reserves have risen dramatically, in 1999 foreign exchange reserves in
China stood at $155 billion, and by 2000 that had gone up $10 billion. In 2005,
it had risen to $800 billion. By the end of 2006, that had gone up to $1 trillion,
and by 2008 it was nearly $2 trillion.
10. The two biggest sectors of
the Chinese economy are agriculture and industry, both of which employ roughly
a total of 70 percent of the labour force and account for roughly 60 percent of
the GDP production in the country.
11. As time goes on, more and
more people will be looking at China, rather than the United States, as
the main driver of the entire world’s economy.
12. China accounts for more than 90% of the world's
rare earth supplies, but has just 23% of global reserves.
Types of Economy
China is now classified as a Transitional Economy. a Transitional economy is an economy which is changing from a centrally planned economy to a free market by undergoing economic liberalisation.
Today, non-State economies account for more than 40 per cent of the country's GDP, while the State-run economy holds a leading position in some key sectors including energy, transportation, telecommunications, the arms industry and high-tech sectors.
During the transition of the past two decades, China has not only achieved rapid economic progress, but also maintained social stability because the pace of reform was kept within an acceptable range for society.
- A joint venture refers to a business agreement in which parties agree to come together and work together on a project.
- Joint ventures in China – as elsewhere - are notoriously difficult to manage successfully. With control shared between often commercially competitive shareholders, the opportunities for conflict are rife.
- However, China's strict commercial laws mean that joint ventures often have to be entered into despite the risks. In certain sensitive economic sectors, wholly foreign-owned enterprises (WFOEs) are not permitted. Foreign companies operating in these sectors have to choose between investing through a joint venture and not investing at all.
- Not all joint ventures are compulsory. Sometimes foreign investors enter into joint ventures for economic or strategic reasons: in order to share risks, costs and resources, or because a particularly influential Chinese partner insists on it. In the acquisition context in particular, Chinese sellers are often unwilling to sell 100% of their equity in the target. Since Chinese sellers can't yet easily take equity in foreign acquirers as a condition of the sale, partial acquisitions are increasingly common.
The unemployment rate in China was last reported at 4.1 % in the first quarter of 2012, with 9 million people registered as unemployed. Yet while the chinese unemployment rate is low by U.S or European standards (Official American unemployment is 9.6%.)
Inflation Rate
 The inflation rate in China was recorded at 3% in May 2012, the most well known measures of inflation are the CPI which measures consumer prices, and the GDP deflator, which measures inflation in the whole of the domestic economy. The char above is of historical data for China inflation rate.
The inflation rate in China was recorded at 3% in May 2012, the most well known measures of inflation are the CPI which measures consumer prices, and the GDP deflator, which measures inflation in the whole of the domestic economy. The char above is of historical data for China inflation rate.
Inflation Rate
 The inflation rate in China was recorded at 3% in May 2012, the most well known measures of inflation are the CPI which measures consumer prices, and the GDP deflator, which measures inflation in the whole of the domestic economy. The char above is of historical data for China inflation rate.
The inflation rate in China was recorded at 3% in May 2012, the most well known measures of inflation are the CPI which measures consumer prices, and the GDP deflator, which measures inflation in the whole of the domestic economy. The char above is of historical data for China inflation rate. Interest Rate

Exchange Rate

Exchange rates play such an important role in a country's competiveness level, currency exchange rates are among the most analysed and forecasted indicators in the world. The exchange rate is determined by the level of supply and demand on the international markets. However, changes in foreign exchange market rates are often difficult to understand and to predict because the market is very large and volatile.
This grap shows that the USD-CNY spot exchange rate appreciated 0.0030 or 0.05 percent during the last few months. Historically, from 1981 until 2012, the USD-CNY averaged 7.0100 reaching an all time high of 8.7300 in January of 1994 and a record low of 1.5300 in January of 1981.
Taxation
- The tax on an individual's income is progressive. As at 2012, an individual's income is taxed progressively at 3% - 45%.
- The 2012 corporate tax rate for domestic and foreign companies is 25%.
- Small companies pay 20% corporate tax in certain cases.
| Tax % | Monthly Income (CNY) |
|---|---|
| 3% | 1 - 1,500 |
| 10% | 1,501-4,500 |
| 20% | 4,501-9,000 |
| 25% | 9,001-35,000 |
| 30% | 35,001-55,000 |
| 35% | 55,001 - 80,000 |
| 45% | 80,001 and above |
Disposable Income
Below is the chart of annual disposable income per capita for urban households in China from year 1991 - 2009:
Annual disposable income per capita for rural households
Below is the chart of annual disposable income per capita for rural households in China from year 1991 - 2009:
- Both graphs show that disposable income and increased over the years for both urban and rural households.
- Using the latest statistics, annual disposable income per capita for urban households is 74% higher than rural households. However, China’s government has been constantly putting in great effort in minimizing the income gap. This can be witnessed in the rising annual disposable income per capita for rural households.



No comments:
Post a Comment